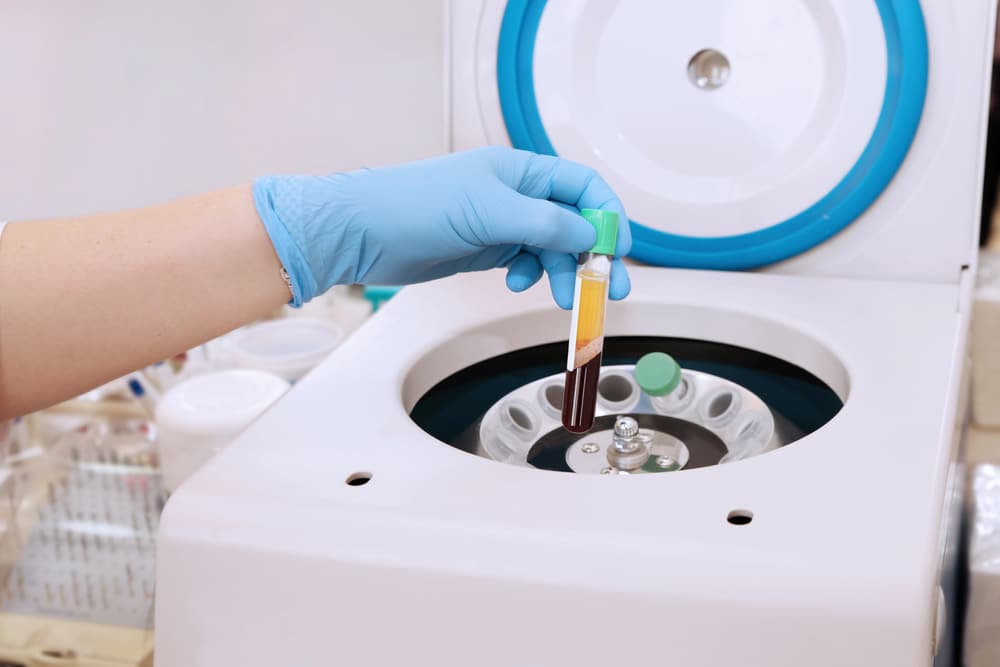
Laboratory filters play a vital role in scientific research, facilitating the removal of particulates from samples in various laboratory applications. According to GlobalSpec’s article “Types of Laboratory Filters,” these filters comprise a filter medium and housing or holder, which support and constrain the filter media in the sample’s path.
Standing at the forefront of filter technology, companies offer a range of innovative solutions to meet diverse laboratory needs. Membrane filters, characterized by thin, polymeric films with microscopic pores, are one of the primary types utilized for quantitative separation or filtration of suspended matter from liquids and gases. Another essential type is centrifugal filters, ideal for small-scale laboratory separations, employing centrifugal force to drive liquid through the filter.
Syringe filters, consisting of a filter element and housing assembly, are crucial for applications requiring sample filtration before entering a syringe. Additionally, specialized and proprietary filters crafted from porous papers cater to specific laboratory requirements.
Selecting laboratory filters involves analyzing both physical and performance specifications. Physical specifications include sample size, pore size, filtration area, and filter shape, while performance specifications encompass flow rate, hold-up volume, particle retention size, porosity, and maximum pressure.
The commitment to innovation in laboratory filtration extends beyond traditional methods, offering configurations tailored to different sample types and filter paper measurement types. With a wide array of filter medium materials and housing materials, including cellulose, ceramic, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), and acrylics, companies ensure versatility and efficiency in laboratory filtration processes.
Click here to learn more about Great Lakes Filters’ products.
Photo and article with all rights reserved, courtesy of globalspec.com