Technical Textiles:
The technical textiles are defined as textile materials and products manufactured primarily for their technical performance and functional properties rather than their aesthetic or decorative characteristics.
Categories of Technical Textile:
Depending on the product characteristics, functional requirements and end-use applications the highly diversified range of technical textile products has been grouped into categories:
- Agro Textiles (Agriculture, horticulture and forestry)
- Building Textiles (Building and construction)
- Clothing Textiles (Components of shoes and clothing)
- Geo Textiles (Geo Textiles, Civil engineering)
- Home Textiles (Components of furniture, household textiles)
- Industrial Textiles (Filtration, cleaning and industrial)
- Medical Textiles (Hygiene and medical)
- Mobile Textiles (Automobiles, shipping, railways)
- Oeko Textiles (Environmental protection)
- Packaging Textiles (Packing materials)
- Protection Textiles (Personal and property protection)
- Sports Textiles (Sport and leisure)
- Aerospace Textiles (aircraft and space textiles)
What is Aerospace?
Aerospace comprises the atmosphere of Earth and surrounding space. Aerospace is actually a compression of
- Aeronautics (the science of flight within Earth’s atmosphere) and
- Space flight (the movement of a vehicle beyond the atmosphere).
Aerospace embraces the full spectrum of flight, and the aerospace industry manufactures the components and equipment for things that fly.
Aerospace Textiles:
From pilot clothing to plane, textile would be anywhere in aircraft. Aerospace textile is an area of technical textiles that covers special finished products to engineered textiles. It includes the textile containing articles for specific functional requirements to work in aircrafts, space suits, space shuttles, lunar and mars mission, and space transportation.
Raw Material for Aero Textile:
Carbon fibre:
It is the material consisting of extremely thin fibres about 0.0002 – 0.0004” in diameter and contains mostly carbon atoms as it is produced as the by-product during the cracking process of crude oil.
- It is also called as graphite fibre.
- Excellent tensile strength.
- Heat resistance.
- Chemical resistance.
Keeping in the view of these properties, these fibres are used as reinforcing moulds, and heat insulating materials.
Apart from this, these fibres are used as raw materials for the manufacture and design of special utility components of aviation machine, space rockets,
Kevlar fibers:
Kevlar is the trade name for Aramid fibres. They are
- Heat resistant
- High strength and modulus.
- Good resistance to abrasion.
- Good fabric integrity even at elevated temperatures.
- Corrosion resistance.
- Malleability.
Kevlar fibres are known for the ability to provide quality and consistency, which are critical for aerospace applications. Kevlar fabrics are used in containment wraps, which perform the important role in preventing the broken engine blades from damaging the aircraft or entering the compartment of the passengers.
Alumina-boria-silica fibres:
Nextel is the trade name for Alumina-boria silica fibers.
- Retain strength.
- Flexibility with little shrinkage even at continuous temperatures up to 2012°F (1100°C).
- Silicon carbide fibre.
- These fibres are similar to carbon fibres.
- Heat resistance.
- Corrosion resistance.
- Elasticity.
- Withstand temperature as high as 1500 degree Celsius.
Nylon fiber:
Nylon 6,6 is made of hexamethylene diamine and adipic acid, which give nylon 6,6 a total of 2 carbons. Heat resistance.
- Friction resistance.
- Melting point of 256 degree celsius.
E- Glass:
E- Glass or electrical grade was originally developed for stand-off insulators for electrical wiring. It was later found to have excellent fiber forming capabilities and is used almost exclusively as the reinforcing phase in the material commonly known as fiberglass or glass fiber.
The essential properties of textile composites in aerospace applications are:
- High specific modulus.
- High specific strength.
- Resistant to chemicals and organic solvents.
- Good fatigue.
- Thermal insulated and thermal resistant.
- Impact and stress resistant.
- Better dimensional stability and conformability.
- Low flammability.
- Non-sensitive to harmful radiations .
Other Properties Required for Aerospace Textiles It is also need to consider incorporating maintainability requirements into aerospace materials. Some of the properties desirable from maintainability point of view are;
- Washable.
- Abrasion resistance.
- Tear resistance.
- Moisture resistance.
- UV stabilization.
- Material standardization.
Based on the applications, textiles used in Aerospace are broadly divided into,
- Aircraft Textiles.
- Space Textiles.
The textile articles being used in aircrafts are mainly for the below purposes.
- Wings, Body parts.
- Curtains.
- Upholstery fabrics.
- Wall covers.
- Head set.
- Floor carpet/covering.
- Seat covers.
Application of Aerospace Textiles:
Evacuation slides:
 |
| Evacuation slides |
Airplane Interiors:
 |
| Airplane Interiors |
Aircraft seat belt:
 |
| Aircraft seat belt |
Aircraft seat cover:
 |
| Aircraft seat cover |
Aircraft Floor Covering:
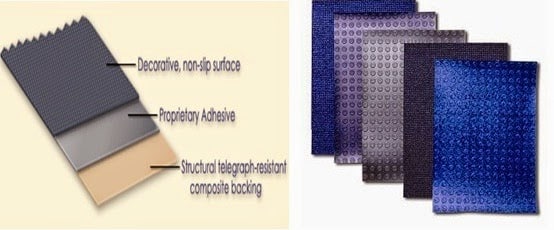 |
| Aircraft Floor Covering |
Uniform of Pilot:
 |
| Uniform of Pilot |
Space suit costume:
 |
| Space suit costume |
Air Bag:
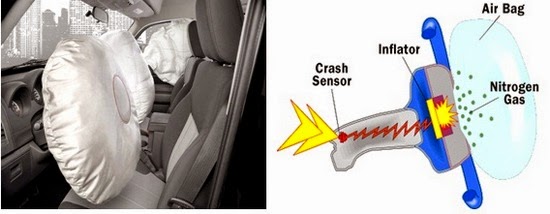 |
| Air Bag |
Pilot parachutes:
 |
| Pilot parachutes |
AeroFlate™ inflateable boat fabric:
 |
| AeroFlate™ inflateable boat fabric |
Life jacket in aircraft:
 |
| Life jacket in aircraft |










