Definition of Fibers:
The essential requirements for fibers to be spun into yarn include a length of at least 5 millimeters, flexibility, cohesiveness, and sufficient strength. Fibres are the foundation for all textile products and can either be natural (natural fibres) or man-made (manufactured or man-made regenerated). Within these two types or groups, there are two main kinds of fibres:
- Fibres of indefinite (very great) length, called filaments.
- Fibres of much shorter length, called staple fibres.
Filaments are generally combined and twisted to form yarns, whilst staple fibres are spun to create yarns. Yarns are then typically woven or knitted into fabrics. A piece of fabric contains a huge number of fibres.
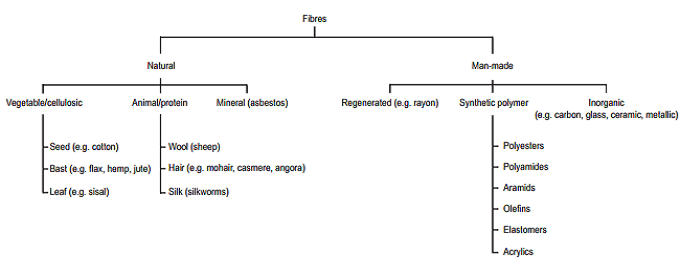
Types of Textile Fibres:
There are three basic types of fibre groups:
- Natural fibres
- Regenerated fibres or man-mad
- Synthetic fibres
Generally Regenerated and synthetic fibres are collectively known as man-made or manufactured fibres.
Natural fibres are occured in nature, such as wool from sheep or cotton from cotton plants where Regenerated fibres are made from natural polymers that are not useable in their original form but can be regenerated (i.e. reformed) to create useful fibres. One of first regenerated fibres was rayon, also referred to as viscose or viscose rayon, regenerated from wood pulp.